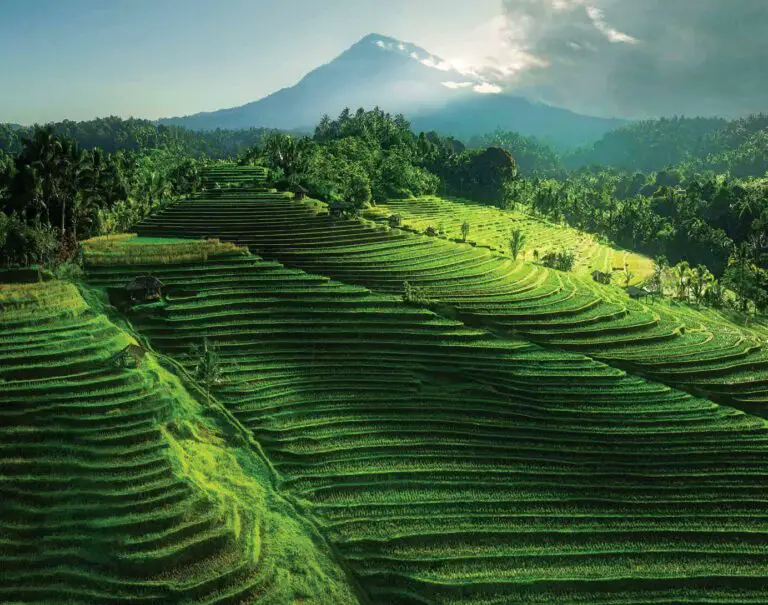
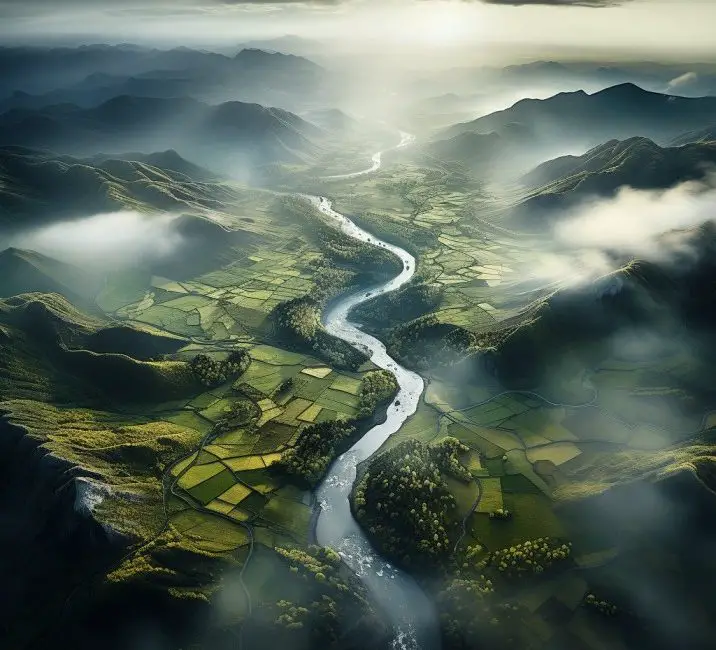
Drone Mapping and Surveying: Utilizing Your Camera for Aerial Mapping Projects
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, or drones, have rapidly transformed from recreational gadgets to powerful professional tools, particularly in the field of mapping and surveying. With advancements in technology and growing accessibility, drone mapping has become an integral part of various industries, from agriculture and construction to urban planning and environmental monitoring.
This in-depth guide is geared towards drone enthusiasts and tech innovators looking to harness the potential of aerial mapping. By focusing on camera utilization and the significance of photography in your drone’s surveying capabilities, this piece aims to provide valuable insights, practical tips, and real-world applications of aerial mapping projects.

The Dawn of Aerial Mapping with Drones
In recent years, the adoption of drones for surveying and mapping has soared. This comes as no surprise, considering the multitude of benefits this technology brings to the table. Among them is the ability to capture high-resolution imagery, data points, and comprehensive 3D models quickly and with reduced effort, all without having to set foot on the surveyed area.
The versatility and cost-effectiveness of drone mapping are reshaping traditional surveying processes. Surveyors, GIS professionals, and other industry experts are increasingly turning to drones as their go-to solution for a wide range of mapping needs.
Benefits Rewarded to Aerial Mappers
Precision Takes Flight
Compared to traditional surveying methods, such as walking the site or using manned aircraft, drones offer unmatched precision. By deploying drones equipped with specialized cameras, surveyors can obtain highly accurate data with centimeter-level detail.
Economical Elevations
The financial aspect is compelling. Drone mapping slashes the costs typically associated with aerial surveying, significantly reducing the need for manpower and time-consuming data collection. What’s more, drones can often provide a quicker turnaround time, bringing efficiency to the next level.
Reaching New Heights
Certain terrains are challenging or dangerous to access, making the surveying process arduous and sometimes impossible. Drones easily maneuver through such landscapes, reaching every nook and cranny without risking human safety.
Capturing the Sky: Your Drone’s Aerial Eye
The camera is at the heart of every drone’s mapping capability. Visual data captured by a drone’s camera is translated into maps, 3D models, point clouds, and orthomosaics. The quality of the camera and the shots it takes directly impact the precision and usability of the data gathered.
Choosing the Right Camera
Define Your Needs
Understanding the specifics of your mapping projects is key. Assess whether you require RGB (standard aerial photography), multispectral (monitoring vegetation health), or thermal cameras (detecting heat sources or temperature differentials).
Camera Quality Matters
Look for drone cameras with adjustable settings, like shutter speed, aperture, and ISO. These settings are particularly valuable when you aim to optimize for lighting conditions and data accuracy.
Compatibility Check
Ensure the camera you choose is robust and compatible with your drone model. This includes the physical mounting as well as the software integration required to extract and process captured data effectively.
Setting the Stage for Success: Aerial Mapping Best Practices
Before your drone takes off, careful planning and preparation set the stage for a successful aerial mapping project. The right strategies will not only improve the quality of the data but will also streamline the entire process.
Strategic Pre-Flight Preparation
Map the Mission
Use specialized drone software to plan the mission, defining the area to be surveyed, the altitudes, and the flight paths your drone will take. This step minimizes ad-hoc decision-making during the flight, ensuring thorough coverage.
Check & Double-Check
Conduct rigorous pre-flight checks on your drone and camera system. Ensure batteries are fully charged, propellers are in good shape, and all systems—mechanical, electrical, and software—are functioning as expected.
In-Flight Data Collection
Fly High, Collect Wide
During the flight, focus on optimal coverage. Maintain a consistent altitude and speed, and keep weather conditions in mind, avoiding strong winds and adverse weather that could affect the drone’s flight stability and image quality.
Overlapping and Grids
Optimize for data processing by capturing images with a high degree of overlap. This redundancy ensures that every part of the area is captured from multiple angles, enhancing 3D reconstruction and model accuracy.
Post-Flight Data Processing
Stitch and Model
Once you have your images, use software to stitch them together into a single, geo-referenced orthomosaic. This final image is accurate to scale and location, making it ideal for detailed analysis and measuring distances on the map.
Analyze and Interpret
Take this analyzed imagery to the next level by creating 3D models and point clouds. Interpret the data for insights that can inform decision-making processes in your project, whether it’s measuring stockpiles, tracking construction progress, or surveying land for precision agriculture.
Case in Point: Successful Stories of Drone Mapping
Precision in Practice
A construction company utilized drone mapping to track progress on a multi-acre site. Over several flights, they captured data that provided the project manager with up-to-date, highly accurate measurements of earthworks and structural development.
Saving the Environment
A wildlife conservation team employed drone mapping to monitor changes in sensitive ecosystems. Regular drone flights enabled them to map and analyze vegetation dynamics and detect illegal activities in remote reserves.
Agriculture of Accuracy
Agricultural experts integrated drone maps with soil samples to produce detailed fertility maps for precision farming. By applying fertilizers and irrigation where and when needed, based on these analyses, they significantly optimized crop yields.
In Conclusion: The Sky’s the Limit for Drone Mappers
The fusion of drone power with advanced mapping and photography techniques brings forth a new era of aerial surveying. It’s more than a technological feat—it’s a gateway to detailed, reliable spatial data that underpins strategic decisions across diverse sectors.
For drone enthusiasts and tech innovators, the message is clear: Mastering the art of aerial mapping with your drone’s camera can unlock a world of opportunities. Whether it’s for professional development, personal projects, or contributing to societal progress, the applications are as extensive as the skies themselves.
By honing in on the capabilities of your camera, employing best practices, and staying abreast of regulations and safety measures, you can take your aerial mapping endeavors to great heights. The future of aerial surveying is here, and it’s looking up—literally.