Mastering the Art of Focus Stacking in Photography
For photographers, capturing a scene in its entirety can sometimes be like trying to tame a dragon — especially when it comes to depth of field. Mastering this elusive concept, which controls the range of sharp focus in an image, can transform your photos from two-dimensional snapshots to rich, lifelike representations of the world as the eye sees it. One technique that has emerged as a powerful ally to conquer depth of field challenges is focus stacking. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the vital practice of focus stacking, providing insights, techniques, and real-world applications to catapult your photography to the next level.
Understanding Focus Stacking
The Essence of Depth in Photography
In photography, depth is perceived when both foreground and background elements are in focus, creating a three-dimensional effect that draws the viewer into the scene. The more elements within varying distances are in focus, the more depth the image appears to have. However, achieving this with a single shot isn’t always possible, particularly in macro or close-up photography.
The Concept of Focus Stacking
Focus stacking, at its core, is a method where multiple images are taken at different focus distances and then combined to create a composite image with a greater depth of field than any of the individual source images. This technique is favored by photographers who require impeccable sharpness over an extended range, which is impossible to obtain in a single shot due to the limitations of any given lens or camera.
The Purpose and Benefits of Focus Stacking
The primary purpose of focus stacking is to extend the range of focus in a photograph, providing sharp details from the foreground to the background. The major benefits include:
- Sharpness across the board: Even in scenes where the depth of field is shallow, focus stacking ensures that everything remains sharply in focus.
- Enhanced clarity and detail: By combining multiple images, photographers can achieve a level of detail not possible with a single shot.
- Creative control: Focus stacking allows for greater flexibility in choosing the focus distance after the shots are taken, and can also be used to create unique visual effects.
Techniques of Focus Stacking
How to Perform Focus Stacking
The process of focus stacking involves several steps:
- Set up your shot: Using a tripod is essential to keep your camera still between each shot.
- Choose your camera settings: Manually set the focus, exposure, and white balance to ensure consistency across all shots.
- Decide on your shot sequence: Plan the number of shots you need and the focus point distance for each.
- Capture your images: Use a remote shutter release to minimize camera shake and adjust the focus slightly for each shot.
- Combine your images: In post-processing, use specialized software to merge the images. Adobe Photoshop and specialized stacking software like Helicon Focus are popular choices.
Software Tools and Equipment Necessary for Focus Stacking
- A digital camera: Any camera that allows manual focus and exposure control will work.
- A sturdy tripod: This provides stability for your camera during shooting.
- A macro lens or extension tubes: These are beneficial for macro photography but are not necessarily required.
- Focus stacking software: While some cameras offer in-camera focus bracketing, dedicated software typically provides more control and better results.
Applications in Photography
Landscape Photography
In the vast landscapes, ensuring sharpness from the flowers in the foreground to the peaks in the distance is a challenge. By taking a series of shots at various focus points and merging them, you can create breathtaking vistas with unparalleled detail.
Macro Photography
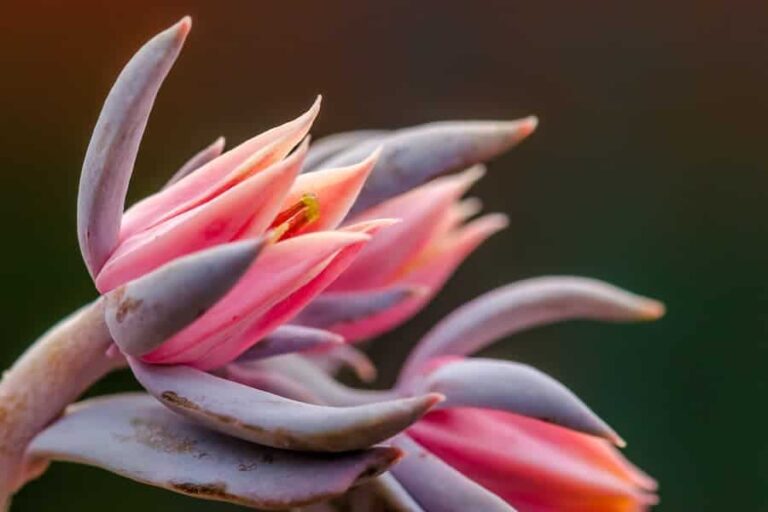
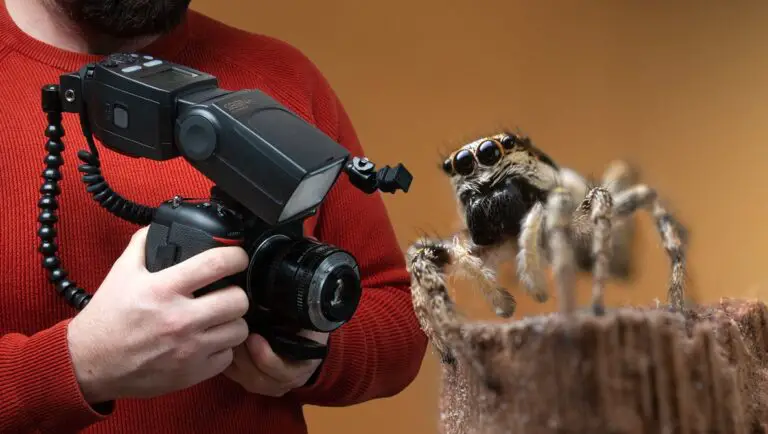
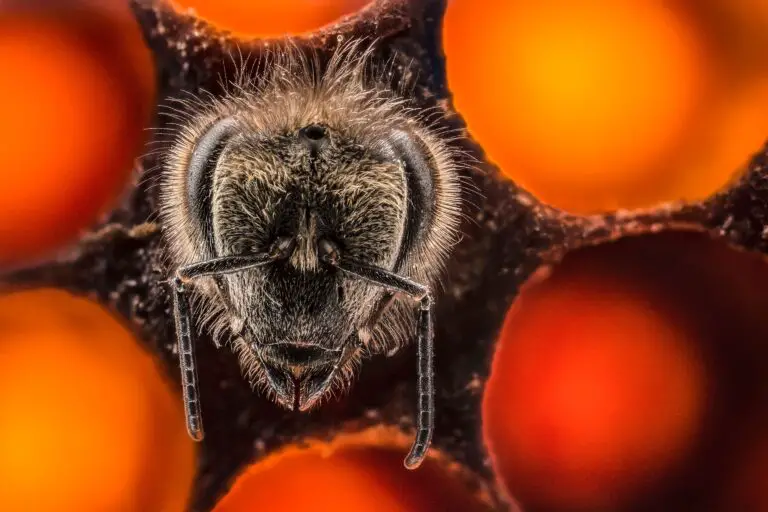
In the world of macro, the tiniest subjects can have vast depth. Focus stacking is indispensable for capturing the intricate patterns on a butterfly’s wing or the fine textures of a flower petal.
Product Photography
When shooting products, clear and sharp detail is paramount. Focus stacking enables you to have the whole product, from front to back, perfectly in focus, showcasing its features in vivid clarity.
Tips for Successful Focus Stacking
Lighting Considerations
Consistent lighting across all images is vital. Use diffused light to minimize harsh shadows and consider the color temperature for a balanced composite.
Composition Tips
Think about how elements in your frame relate to each other. Decide which parts of the scene must be in focus to tell the story you want to convey in your image.
Post-Processing Techniques
Use layer masks in software like Photoshop for more intricate control over which parts of an image should be in focus. Adjust the opacity to blend edges and details seamlessly.
Case Studies or Examples
Landscape Photography Success Story
A renowned landscape photographer shares how using focus stacking transformed their shots from mundane to mesmerizing, with glowing testimonials from astounded viewers.
Macro Photography Before and After
A side-by-side comparison shows the stark difference between a normal macro shot and one produced with focus stacking, emphasizing the incredible detail and sharpness achievable with this technique.

Conclusion
Despite its complexity, focus stacking offers a myriad of benefits that can drastically elevate the quality of your photographs. By mastering this skill, you ensure that your images resonate with a crispness and clarity that captures the true essence of the scene. Whether it’s the expansive depth of a sprawling landscape or the intricate details of a minuscule subject, the art of focus stacking empowers photographers to bring their creative vision to life with unparalleled sharpness. I encourage you to experiment with focus stacking, as it is not only a technical marvel but also a gateway to a new world of visual storytelling.